v3.0, Release 28/07/2008
Table of Contents
- How can I participate ?
- How can I create a community?
- How can I enter a community?
- How can I communicate with other members?
- How can I create a workspace?
- How can I open a workspace?
- What items can be added to an workspace?
- How can I add items to a workspace?
- What can I do in a workspace?
- How can I navigate easily in a workspace?
- How does a workspace evolve?
- Switching to a formal projection
- How can I import an existing discussion forum?
How can I participate ? [back to ToC] [Video Presentation]
How can I create a community? [back to ToC]
All CoPe_it! participants are members of at least one community. When participants initially sign up, they belong to Earth the default community (to which all CoPe_it! participants belong). Every community has a moderator who is in charge of managing its workspaces and accept / reject participation requests from participants that do not belong to the community.
The creation of new communities can be done by using the appropriate option from the main menu, as depicted in the screenshot below. After filling in the form the participant is notified that the community has been created and is given instructions on how to add members to it. The system assigns the role of Community Administrator to the creator.
How can I enter a community? [back to ToC]
If a participant is a member of a particular community, he/she may enter it by using the Switch Community option in either the Quick Links or the Actions menu, as shown below.
If a participant is not a member of a particular community, and he/she desires to eneter it, he/she has first to request permission from the Community Administrator (see screenshot below). Community Administrator will be immediately notified in order to handle the particular request.
How can I communicate with other members? [back to ToC]
This release of CoPe_it! supports communication only through email. One has to click on the member he/she wants to communicate with (bottom left pane) and select the Mail option.
How can I create a workspace? [back to ToC]
How can I open a workspace? [back to ToC]
What items can be added on a workspace? [back to ToC]
How can I add items to a workspace? [back to ToC] [Video Presentation]
What can I do in a workspace? [back to ToC]
[Video Presentation: How to create a relationship]
[Video Presentation: How to group items]
Click the Mini Map button or the bottom right corner of a workspace and navigate by dragging the red box or clicking on the area you want to move.
How does a workspace evolve? [back to ToC]
CoPe_it! participants may easily create and upload various types of knowledge items; these can be either existing multimedia resources (the content of which can be displayed upon request or can be directly embedded in the workspace) or dedicated item types such as ideas, notes and comments. All the above items can be interrelated by trouble-free actions (as in the case of their creation and uploading, such actions are performed through the mouse). When interrelating items, participants may select the color of the connecting arrow and provide (if they wish) a legend describing the interrelationship they conceive. These legends are intentionally arbitrary (see figure below).
During the evolution of an argumentative collaboration, additional ideas (coresponding to alternative solutions) may occur and images as well as videos can be embedded into the workspace. The colored rectangles in the figure below have been created by participants to cluster related items (the two rectangles shown correspond to the two alternative ideas proposed so far) making it easier to identify the available alternatives.
Switching to a formal projection [back to ToC] [Video Presentation]
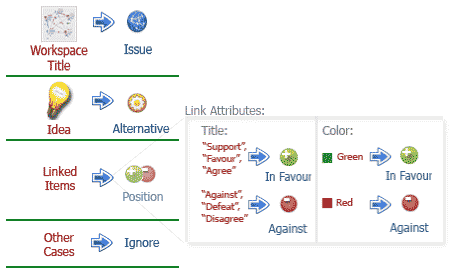
The transformation from an informal to a formal projection is being executed according to the following set of rules:
The formal projection of a collaboration space aims mainly at the exploitation of information by the machine (machine-interpretable view). Formal projections provide a fixed set of discourse element and relationship types, with predetermined, system interpretable semantics.
The knowledge items allowed in this projection are issues, alternatives, positions, and preferences. Issues correspond to problems to be solved, decisions to be made, or goals to be achieved. For each issue, participants may propose alternatives (i.e. solutions to the problem under consideration) that correspond to potential choices. Positions are asserted in order to support the selection of a specific course of action (alternative), or avert the participants’ interest from it by expressing some objection. A position may also refer to another (previously asserted) position, thus arguing in favor or against it. Finally, preferences provide individuals with a qualitative way to weigh reasons for and against the selection of a certain course of action. A preference is a tuple of the form [position, relation, position], where the relation can be “more important than” or “of equal importance to” or “less important than”. The above four types of items enable participants to contribute their knowledge on the particular problem or need (by entering issues, alternatives and positions) and also to express their relevant values, interests and expectations (by entering positions and preferences).
In the formal projection, the collaboration items follow a tree structure where the following rules apply:
- Issue (root of the tree) is the name of the collaboration space
- Alternatives (nodes of 2nd degree) are the ideas being produced in the desktop view
- All items linked to the ideas are parsed (like a genetic tree) to complete the tree structure and are handled as positions. On the produced tree, the relationship parent-child may be either positive or negative (argument in favor or against). This information is extracted, through parsing relationships in the desktop view (this is performed by following some transformation rules:
- Links with caption "support", "favor", "agree" are considered to be positive arguments.
- Links with caption "against", "defeats", "disagree" are considered to be negative arguments
- Links with green color refer to a positive argument, whereas links with red color refer to a negative argument
- Links with any other color are considered as "neutral" positions and are ignored.
How can I import an existing discussion forum? [back to ToC]
CoPe_it! permits importing entire discussions available in forums found on the web. During the import, a new workspace is created and every message in the discussion forum appears as a separate item on the workspace. Currently, CoPe_it! supports the import of phpNuke based forums (more forum types will be covered in future releases). The figure below shows how a participant can request the import of a web forum.
On has to keep in mind the following:
- The "Forum URL" input should refer to a forum topic. Otherwise the import cannot proceed.
- Since the title for the individual forum items that are imported on a workspace are extracted automatically (by parsing the forum's HTML pages), some titles of items may either be missing or contain non-readable excerpts. Future versions will overcome these issues.

